Swimming is a fantastic full-body workout that engages and strengthens various muscle groups. Whether you’re a professional swimmer or simply enjoy swimming as a recreational activity, understanding the muscles that come into play can help you maximize the benefits of your swimming workouts. In this comprehensive article, we will explore in detail the muscles that swimming works, providing you with valuable insights on how swimming can contribute to overall muscle development and fitness.
The Core Muscles
Swimming is renowned for its ability to target and strengthen the core muscles. The core muscles include the abdominal muscles (rectus abdominis, transversus abdominis, and obliques), the lower back muscles (erector spinae), and the muscles around the pelvis (hip flexors). These muscles play a vital role in maintaining stability, posture, and balance in the water. As you swim, these core muscles are constantly engaged to provide the necessary stability and power for efficient movement through the water.
Upper Body Muscles
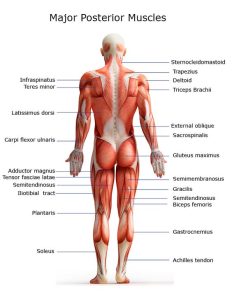
Swimming is an excellent workout for the upper body, targeting the muscles of the arms, shoulders, and upper back. The primary muscles worked during swimming include the deltoids (shoulder muscles), pectoralis major (chest muscles), latissimus dorsi (back muscles), and trapezius (upper back and neck muscles). These muscles are responsible for propelling your body forward in the water and executing the different swimming strokes. Frequent swimming can lead to increased strength and tone in these upper body muscles, enhancing overall upper body strength and definition.
Lower Body Muscles
While swimming predominantly involves the upper body, the lower body muscles also play a significant role in maintaining proper body position and propulsion. The main muscles worked during swimming in the lower body include the quadriceps (front of the thighs), hamstrings (back of the thighs), gluteal muscles (buttocks), and calf muscles. These muscles work together to provide stability, balance, and kicking power. Regular swimming can lead to improved lower body strength, endurance, and muscle tone.
Cardiovascular Fitness
In addition to its muscle-strengthening benefits, swimming is an excellent cardiovascular exercise. It elevates your heart rate, improving cardiovascular fitness and endurance. By continuously moving against the resistance of the water, your heart and lungs have to work harder to deliver oxygen to the working muscles. This sustained cardiovascular activity helps improve the efficiency of your heart and lungs, contributing to overall cardiovascular health.
Muscle Balance and Flexibility
Swimming is a low-impact exercise that allows for a wide range of motion in the joints. This promotes muscle balance and flexibility throughout the body. As you perform different swimming strokes, your muscles lengthen and contract, improving overall flexibility. Regular swimming can help prevent muscle imbalances and promote a balanced musculoskeletal system.

Incorporating Different Strokes for Maximum Benefit
To fully engage different muscle groups, it is beneficial to incorporate various swimming strokes into your routine. The four primary swimming strokes include freestyle (front crawl), backstroke, breaststroke, and butterfly. Each stroke targets specific muscle groups differently, allowing you to work all major muscle groups in your body.
Freestyle: Freestyle primarily works the upper body muscles, including the shoulders, arms, and upper back.
Backstroke: Backstroke engages similar muscles to freestyle, focusing on the posterior chain, including the back and triceps.
Breaststroke: Breaststroke places more emphasis on the leg muscles, including the quadriceps, hamstrings, and glutes.
Butterfly: Butterfly is a demanding stroke that engages the upper body muscles extensively, including the chest, shoulders, and triceps.
Incorporating all four swimming strokes into your routine can provide a well-rounded workout that targets all major muscle groups while promoting overall strength and endurance.
Conclusion
Swimming is a highly effective full-body workout that engages and strengthens various muscle groups. From the core muscles to the upper and lower body muscles, swimming provides a comprehensive and balanced approach to muscle development and overall fitness. By regularly incorporating swimming into your exercise routine and incorporating different strokes, you can achieve improved muscle strength, endurance, and flexibility. So dive in, reap the benefits, and enjoy swimming as a fantastic way to work your muscles and enhance your overall fitness level.


